Sustainability analytics & ESG reporting platform
Track environmental impact, social responsibility, and governance practices with advanced analytics.

Align your business with ESG reporting requirements
Meet the strict compliance requirements relevant to your business with the help of data analytics software.
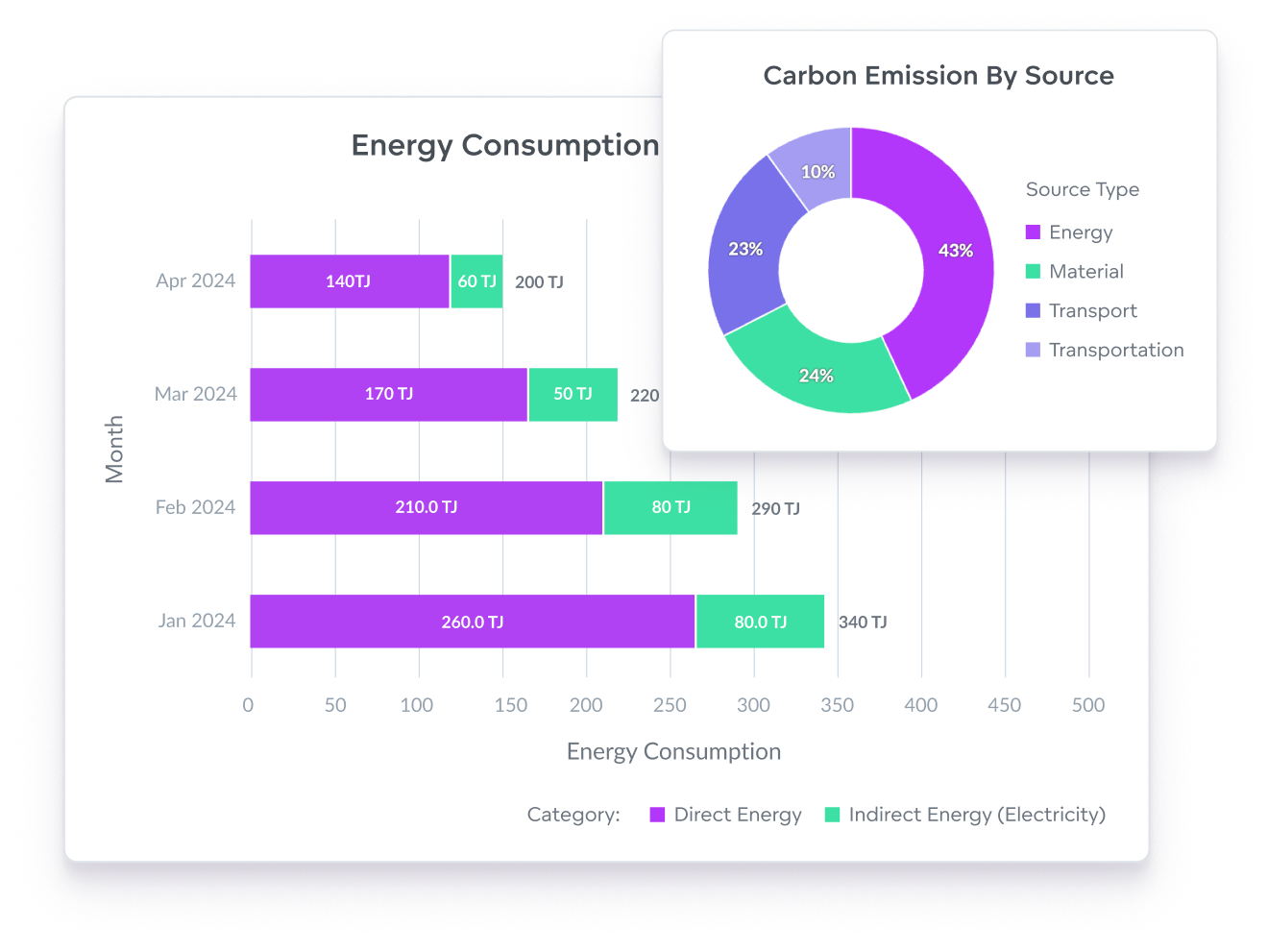
Control your environmental footprint
- Track and report carbon emissions, air and water pollution, deforestation, green energy initiatives, waste management, water usage, and more.
- Monitor multiple data sets from disparate sources in one central location.
- Utilize modern BI capabilities, automation, and AI to understand trends, spot anomalies, and forecast future developments.
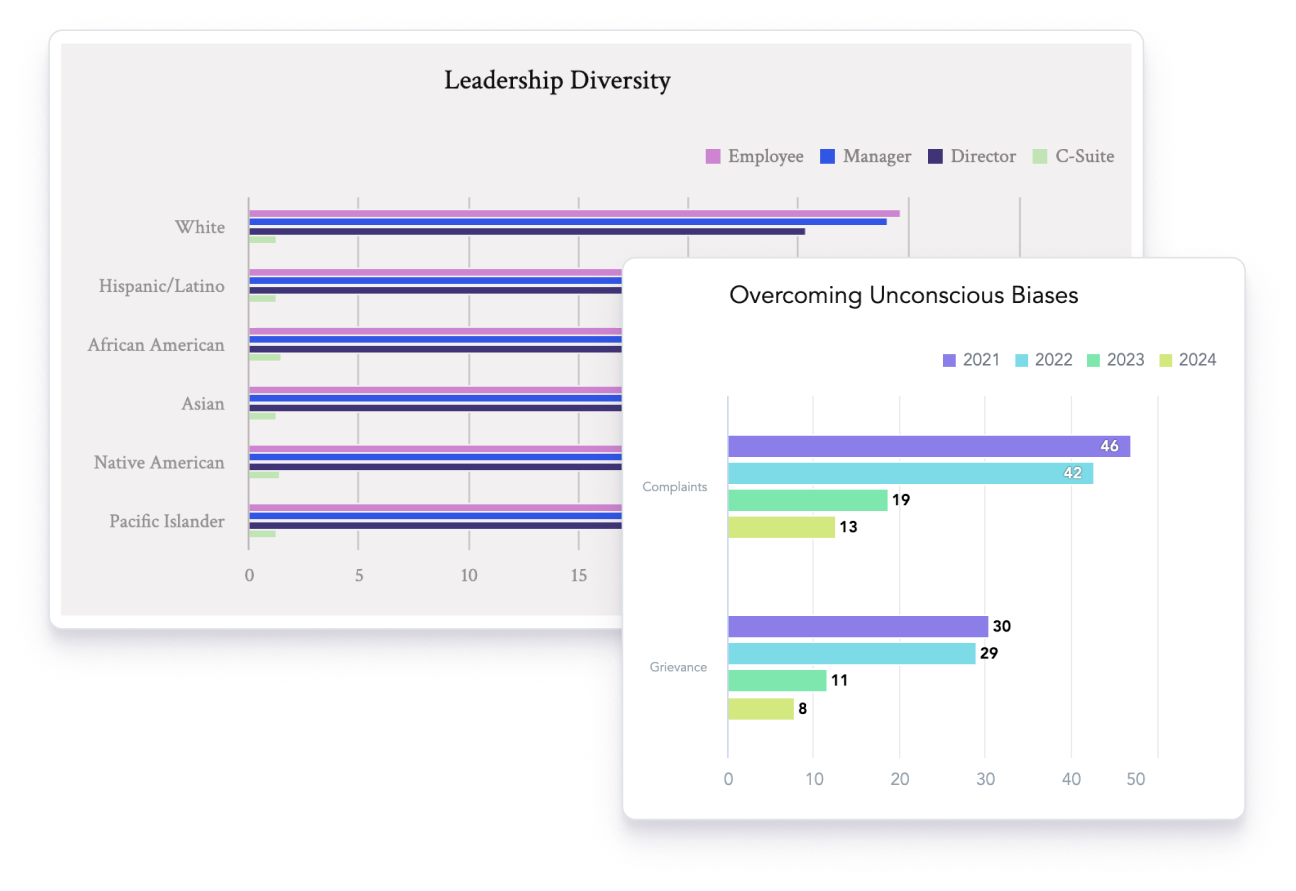
Analyze social responsibility projects
- Get granular insights into labor-related agendas, including employee rights, fair wages, diversity and inclusion, and health and safety.
- Report positive community engagement with an easy-to-use, drag-and-drop interface.
- Leverage modern BI capabilities and AI to improve operational efficiency and identify areas for cost reduction.
Track and report governance practices
- Efficiently analyze corporate governance projects, ethical practices, and risk management data — and their relative impact.
- Easily create modern reports and interactive dashboards.
- Seamlessly embed your analytics exactly where your customers and stakeholders need it.
Dive deep into our success stories
Examples of ESG and sustainability dashboards
Explore how data analytics helps companies with ESG reporting.
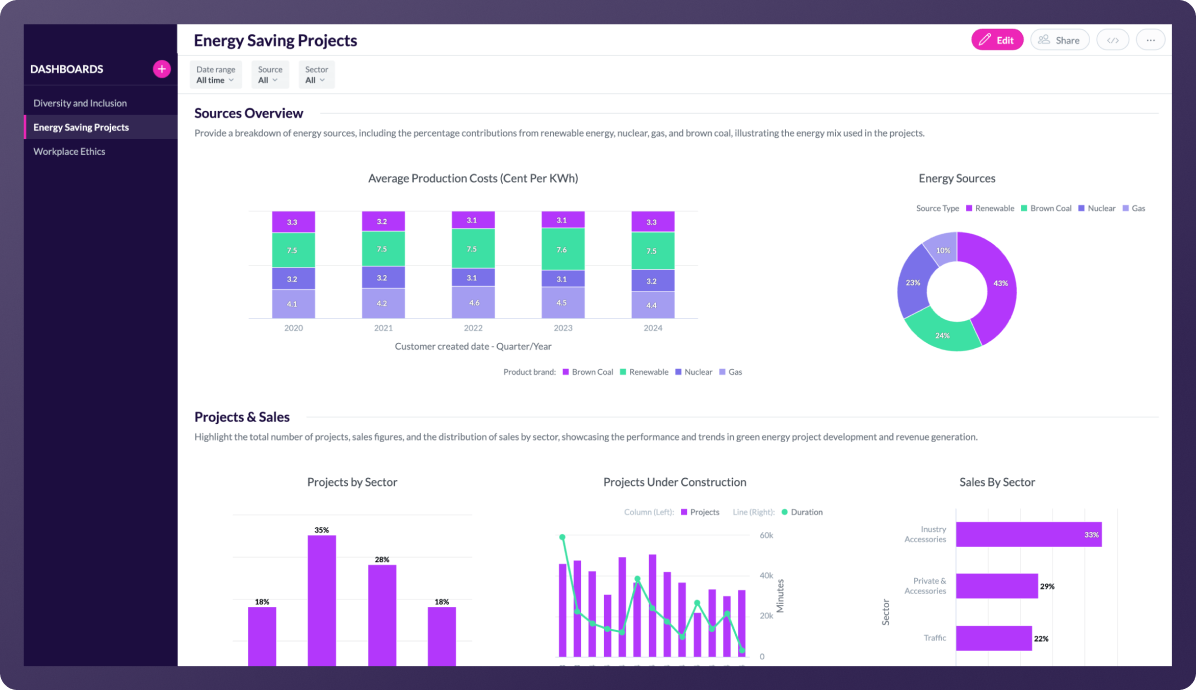
Energy saving projects at-a-glance
Organizations can gain a comprehensive overview of their green energy projects and break them down into detailed insights for a clearer understanding of their status.
- Drill into data to reveal more granular project details.
- Create and customize real-time, ESG insights.
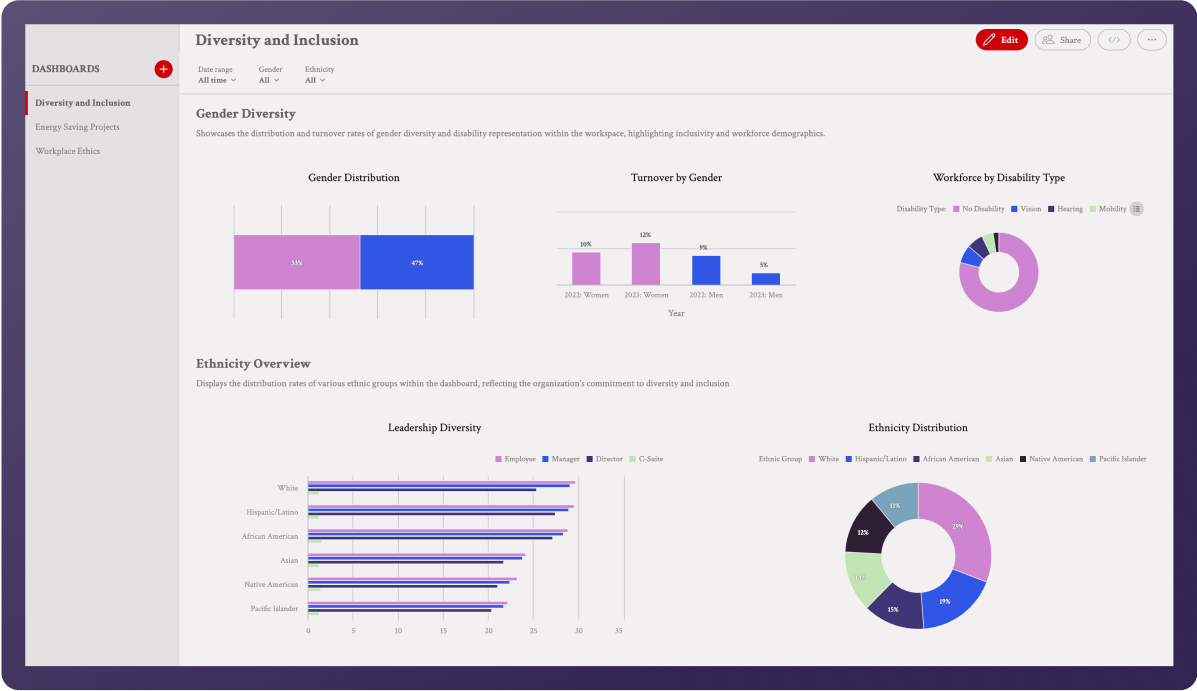
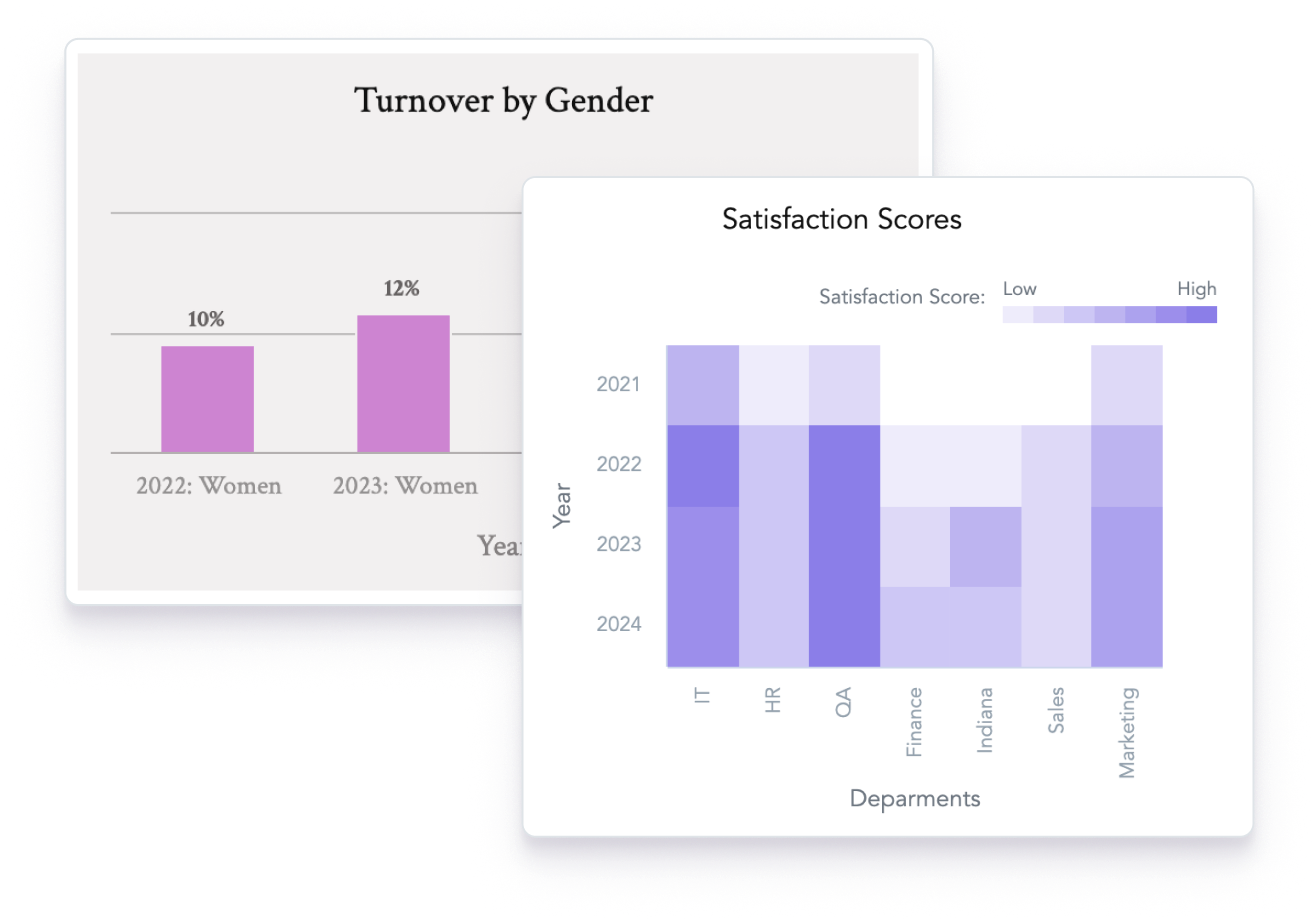
Overview of diversity and inclusion
A D&I dashboard can cover various aspects, including internal mobility trends, annual performance evaluations, and employee engagement levels, providing a detailed view of diversity and inclusion efforts within an organization.
- Easy to share with management and stakeholders.
- Seamlessly embeds into your current software set up.
Discuss your use case with us
See how GoodData can help with your analytics goals.
Why choose our analytics platform?
Reasons why companies love our analytics platform include:
Smoothly implement in your ecosystem



Deploy in GoodData Cloud
GoodData Cloud is a SaaS product operated and maintained by us. Customers receive continuous code updates and it can be deployed in AWS, Azure, and multi-region.


Deploy Self-hosted
Self-hosted uses the same codebase as GoodData Cloud and is ideal for users needing enhanced security, governance, or control for data residency or regulatory compliance.




Integration
Open APIs and declarative SDKs — connect to code repositories and 3rd-party apps, embed anywhere.




Security and governance
Trusted analytics — certifications, inherited permissions, and cascading content changes for easy admin.



Accessibility
Accessible analytics — ensuring compliance and delivering inclusive experiences.















A trusted platform, loved by users






Common questions about ESG analytics
ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) reporting refers to the disclosure of data that covers a company’s operations in three key areas: environmental impact, social responsibility, and governance practices. This reporting aims to provide transparency to stakeholders (including investors, customers, employees, and regulators) about how a company manages risks and opportunities related to these areas.
There are three components of ESG Reporting:
Environmental:
- Climate Change: carbon footprint, greenhouse gas emissions, energy usage, and renewable energy adoption.
- Resource Management: water usage, waste management, recycling, and sustainable resource sourcing.
- Biodiversity: impact on natural habitats and efforts to protect ecosystems.
Social:
- Labor Practices: employee rights, fair wages, diversity and inclusion, health and safety.
- Community engagement: Philanthropy, community development, and relationships with local communities.
- Product responsibility: safety standards, ethical marketing, and customer privacy.
Governance:
- Corporate Governance: board structure, executive compensation, shareholder rights.
- Ethical Practices: anti-corruption policies, business ethics, transparency.
- Risk Management: systems in place for managing financial and non-financial risks.
The many benefits of ESG reporting include:
- Investor Confidence: helps attract and retain investors by demonstrating a commitment to sustainable and ethical practices.
- Regulatory Compliance: ensures compliance with increasing regulatory requirements on sustainability.
- Brand Reputation: improves the company’s reputation among consumers and other stakeholders.
- Operational Efficiency: identifies areas for improving efficiency and reducing costs.
By implementing robust ESG reporting practices, companies can better manage their impact on the environment and society while strengthening their governance structures.
ESG reporting process consists of the following five steps:
- Assessment: identifying relevant ESG issues and metrics.
- Data Collection: gathering quantitative and qualitative data from various sources within the organization.
- Analysis: analyzing data to assess performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Reporting: compiling and disclosing information in a structured format, often using established frameworks and standards.
- Communication: sharing the report with stakeholders through various channels, including annual reports, sustainability reports, and corporate websites.
Some of the most widely used ESG reporting standards are:
- Global Reporting Initiative (GRI): provides guidelines for sustainability reporting.
- Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB): focuses on financially material sustainability information for investors.
- Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD): provides a framework for disclosing climate-related financial risks.
- UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): aligns reporting with global goals for sustainable development.
ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) reporting and sustainability analytics are important for several reasons:
- Risk management: ESG reporting helps companies identify potential environmental, social, and governance risks that could impact their operations, reputation, and financial performance. By understanding these risks, companies can implement strategies to mitigate them, ensuring long-term sustainability and reducing the likelihood of costly incidents.
- Investor confidence and access to capital: Investors are increasingly considering ESG factors when making investment decisions. Companies with strong ESG performance are more attractive to investors seeking sustainable and responsible investments. Plus, companies with robust ESG practices may benefit from a lower cost of capital, as they are perceived as less risky and more stable investments.
- Regulatory compliance: Governments and regulatory bodies are imposing stricter requirements related to environmental protection, social responsibility, and corporate governance. ESG reporting ensures compliance with these regulations. Non-compliance can result in legal penalties, fines, and reputational damage. ESG reporting helps avoid these consequences by demonstrating adherence to regulatory standards.
- Reputation and brand value: Customers, employees, and other stakeholders view companies that are transparent about their ESG practices more favorably. ESG reporting builds trust and credibility, showing that a company is dedicated to ethical practices and long-term sustainability.
- Operational efficiency and cost savings: Sustainability analytics can identify areas where resources can be used more efficiently, reducing waste and lowering costs. By optimizing energy usage and resource management, companies can achieve significant cost savings while minimizing their environmental impact.
- Innovation and long-term value creation: Focusing on sustainability can drive innovation, as companies develop new products, services, and processes that are environmentally friendly and socially responsible. ESG practices support long-term value creation by ensuring that business growth does not come at the expense of the environment or society.
Understanding how ESG reporting impacts individual industries is crucial for identifying sector-specific challenges and opportunities. Below are some examples of how different industries are adapting to and benefiting from ESG reporting.
- Real estate: The environmental aspect of ESG reporting in the real estate industry focuses on promoting sustainable development and resource efficiency. This includes the adoption of green building practices, such as energy-efficient designs, the use of renewable energy sources, and sustainable materials. By prioritizing the efficient use of water, energy, and other resources, real estate companies can significantly reduce their environmental footprint. Additionally, ESG reporting ensures compliance with environmental regulations and standards, like LEED or BREEAM, and helps in identifying and mitigating environmental risks, contributing to long-term sustainability and the resilience of real estate assets.
- Banking and financial services: Banks and financial institutions are increasingly integrating ESG criteria into their lending and investment decisions to mitigate risks associated with environmental, social, and governance factors. This shift not only aligns with regulatory expectations and investor demands for sustainable practices but also promotes long-term financial stability. By prioritizing ESG considerations, financial institutions can better assess credit risk, improve stakeholder trust, and capitalize on emerging opportunities in green finance, thereby fostering a more resilient and ethically responsible financial ecosystem.
- Healthcare: ESG reporting significantly impacts the healthcare industry by promoting sustainability, enhancing patient care, and ensuring regulatory compliance. By integrating ESG criteria, healthcare organizations can reduce their environmental footprint through energy-efficient facilities, waste management, and sustainable procurement practices. Socially, ESG reporting emphasizes patient safety, equitable access to care, and community health initiatives, thereby improving overall healthcare outcomes. Governance aspects ensure transparency, ethical practices, and robust management structures, fostering trust and accountability. Ultimately, ESG reporting helps healthcare providers align their operations with broader societal goals, attracting socially responsible investors and enhancing their reputation and long-term viability.
- Supply Chain: By adopting ESG criteria, companies are encouraged to minimize their environmental impact through energy-efficient logistics, sustainable sourcing, and waste reduction initiatives. Socially, ESG reporting ensures fair labor practices, safe working conditions, and community engagement, fostering a more responsible and equitable supply chain. Governance aspects enhance accountability and risk management, ensuring that supply chain operations comply with regulations and ethical standards. Ultimately, ESG reporting helps build resilient, sustainable, and socially responsible supply chains that meet the growing demands of consumers, investors, and regulators.
Try GoodData yourself
See how GoodData can help with your analytics goals