Create a Vertica Data Source
Follow these steps to connect to Vertica and create a Vertica data source:
Refer to Additional Information for additional performance tips and information about Vertica feature support.
Configure User Access Rights
We recommend creating a dedicated user and user role specifically for integrating with GoodData.
Steps:
Create a user role and grant it the following access rights:
GRANT USAGE, SELECT ON SCHEMA {schema_name} TO ROLE {role_name}; GRANT SELECT ON ALL TABLES IN SCHEMA {schema_name};Create a user and assign them the user role:
GRANT ROLE {role_name} TO USER {user_name};Make the user role default for the user:
ALTER USER {user_name} SET DEFAULT_ROLE={role_name};
Create a Vertica Data Source
Once you have configured your Vertica user’s access rights, you can proceed to create a Vertica data source that you can then connect to.
Steps:
On the home page switch to Data sources.
Click Connect data.
Select Vertica.
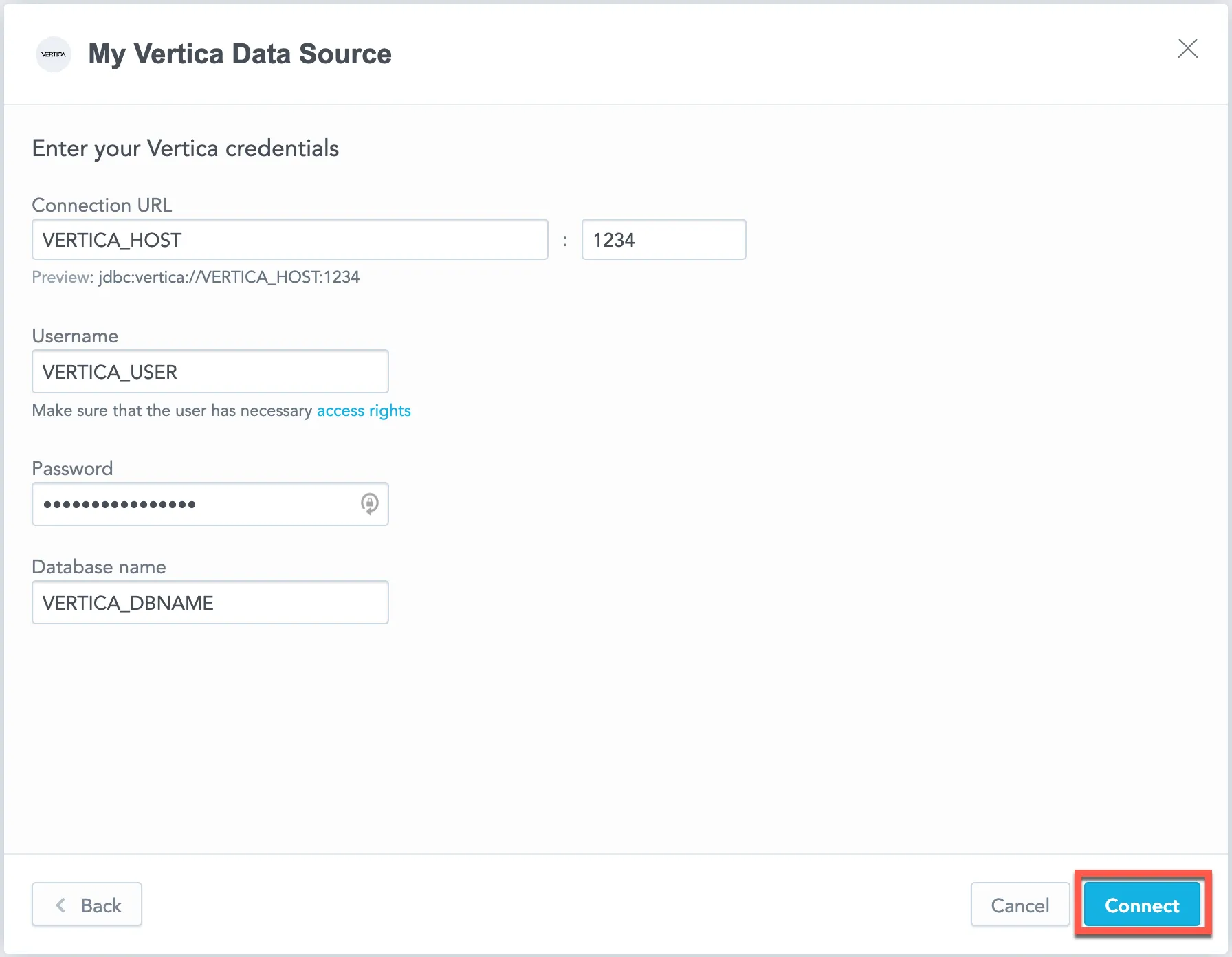
Name your data source and fill in your Vertica credentials and click Connect:
Input your schema name and click Save:
Your data source is created!
Steps:
Create a Vertica data source with the following API call:
curl $HOST_URL/api/v1/entities/dataSources \ -H "Content-Type: application/vnd.gooddata.api+json" \ -H "Accept: application/vnd.gooddata.api+json" \ -H "Authorization: Bearer $API_TOKEN" \ -X POST \ -d '{ "data": { "type": "dataSource", "id": "<unique_id_for_the_data_source>", "attributes": { "name": "<data_source_display_name>", "url": "jdbc:vertica://<VERTICA_HOST>:5432/<VERTICA_DBNAME>", "schema": "<VERTICA_SCHEMA>", "type": "VERTICA", "username": "<VERTICA_USER>", "password": "<VERTICA_PASSWORD>" } } }' | jq .To confirm that the data source has been created, ensure the server returns the following response:
{ "data": { "type": "dataSource", "id": "<unique_id_for_the_data_source>", "attributes": { "name": "<data_source_display_name>", "url": "jdbc:vertica://<VERTICA_HOST>:5432/<VERTICA_DBNAME>", "schema": "<VERTICA_SCHEMA>", "type": "VERTICA", "username": "<VERTICA_USER>" } }, "links": { "self": "$HOST_URL/api/v1/entities/dataSources/<unique_id_for_the_data_source>" } }
Create a Vertica data source with the following API call:
from gooddata_sdk import GoodDataSdk, CatalogDataSource, BasicCredentials
host = "<GOODDATA_URI>"
token = "<API_TOKEN>"
sdk = GoodDataSdk.create(host, token)
sdk.catalog_data_source.create_or_update_data_source(
CatalogDataSourceVertica(
id=data_source_id,
name=data_source_name,
db_specific_attributes=VerticaAttributes(
host=os.environ["VERTICA_HOST"],
db_name=os.environ["VERTICA_DBNAME"]
),
schema=os.environ["VERTICA_SCHEMA"],
credentials=BasicCredentials(
username=os.environ["VERTICA_USER"],
password=os.environ["VERTICA_PASSWORD"],
),
)
)
Additional Information
Ensure you understand the following limitations and recommended practice.
Data Source Details
Database versions 9.0 and newer are supported.
GoodData uses an up-to-date JDBC client driver.
The JDBC URL must be in the following format:
jdbc:vertica://<host>:<port>/<databaseName>For security reasons, the query in the JDBC URL must not contain theDisableCopyLocalandTrustStorePathparameters.Basic authentication is supported. Specify
userandpassword.If you use native authentication inside your cloud platform (for example, Google Cloud Platform, Amazon Web Services, or Microsoft Azure), you do not have to provide the username and password.
Workspaces that use Vertica as a data source have access to the following additional features:
- You can use APPROXIMATE_COUNT functions in Analytical Designer and MAQL. For more information, see APPROXIMATE_COUNT.
- You can use Data Sampling in Analytical Designer and through the API. For more information, see Data Sampling. Please note that Vertica started to support TABLESAMPLE for views from version 10.0.1, using view data sampling on older versions of Vertica will result in an error.
Performance Tips
If your database holds a large amount of data, consider the following practices:
Denormalize the relational model of your data base.
You can use flatten tables (See the Flattened Tables section of the Vertica documentation for details) to assist with denormalization. Because Vertica is a columnar database, queries read only the required columns, and each column is compressed separately.
Optimize projections (See the Working with Projections section of the Vertica documentation for details).
- RESEGMENT by the columns that are most frequently used for JOIN and aggregation operations. You can also RESEGMENT by a column with high cardinality so that loaded data is evenly distributed in your cluster.
- SORT by the columns that are most frequently used for JOIN and aggregation operations. Those columns are typically mapped to the attributes that are most frequently used for aggregations in visualizations.
- Use RLE encoding for low-cardinality columns (columns with few distinct values). See the Encoding Types section of the Vertica documentation for details.
- If you have to build analytics for multiple, mutually exclusive use cases, define multiple projections on top of a table.
Utilize live aggregate projections. See the Pre-Aggregating Data in Projections section of the Vertica documentation for details. Live aggregate projections can store pre-aggregated data when using additive functions like COUNT or SUM. Vertica automatically selects the most optimal projection to use. This may help you simplify your logical data model (LDM). Instead of declaring both the full and pre-aggregated datasets, you can create standard and pre-aggregated projections on top of single table, declare only a single dataset in your LDM, and map that dataset to the table.
Use hierarchical partitioning to avoid too many partitions (ROS containers) in a single projection. See the Partitioning Tables section of the Vertica documentation for details.
Use Eon Mode to spin up sub-clusters based on user needs. See the Using Eon Mode section of the Vertica documentation for details.
- Users with similar needs populate data into EON depots that are likely to be reused.
- Isolate data transformation operations running in your database from the analytics generated by GoodData.
Scale up based on users needs. Automate adding and removing secondary sub-clusters.
Query Timeout
The default timeout value for queries is 160 seconds. If a query takes longer than 160 seconds, it is stopped. The user then receives a status code 400 and the message Query timeout occurred.
Query timeout is closely related to the ACK timeout. For proper system configuration, the ACK timeout should be longer than the query timeout. The default ACK timeout value is 170 seconds.
Permitted parameters
- TLSmode