Create an Oracle Database Data Source
Beta Feature
Oracle Database data source is currently a beta feature and is still under active development. Do not use beta features in your production environment.
Follow these steps to connect to an Oracle Database and create an Oracle Database data source:
Refer to Additional Information for additional performance tips and information about Oracle Database feature support.
Configure User Access Rights
We recommend creating a dedicated user and user role specifically for integrating with GoodData.
Steps:
Create a user role and grant it access rights:
CREATE ROLE {role_name}; GRANT SELECT ON {schema_name}.{table_name} TO {role_name}; GRANT SELECT ON v$session TO {role_name};Create a user and assign them the user role:
CREATE USER {user_name} IDENTIFIED BY {password}; GRANT {role_name} TO {user_name};Make the user role default for the user:
ALTER USER {user_name} DEFAULT ROLE {role_name};
Create an Oracle Database Data Source
Once you have configured your Oracle Database user’s access rights, you can proceed to create a Oracle Database data source that you can then connect to.
Steps:
On the home page switch to Data sources.
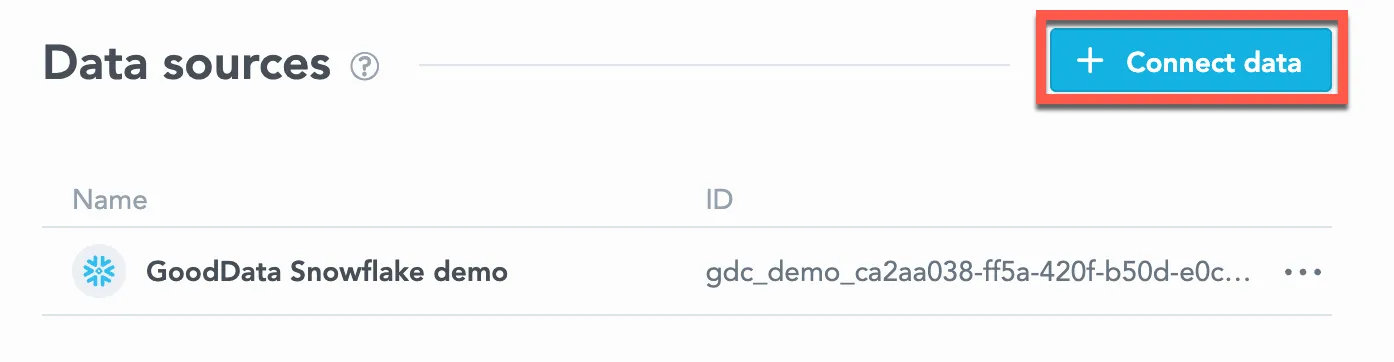
Click Connect data.
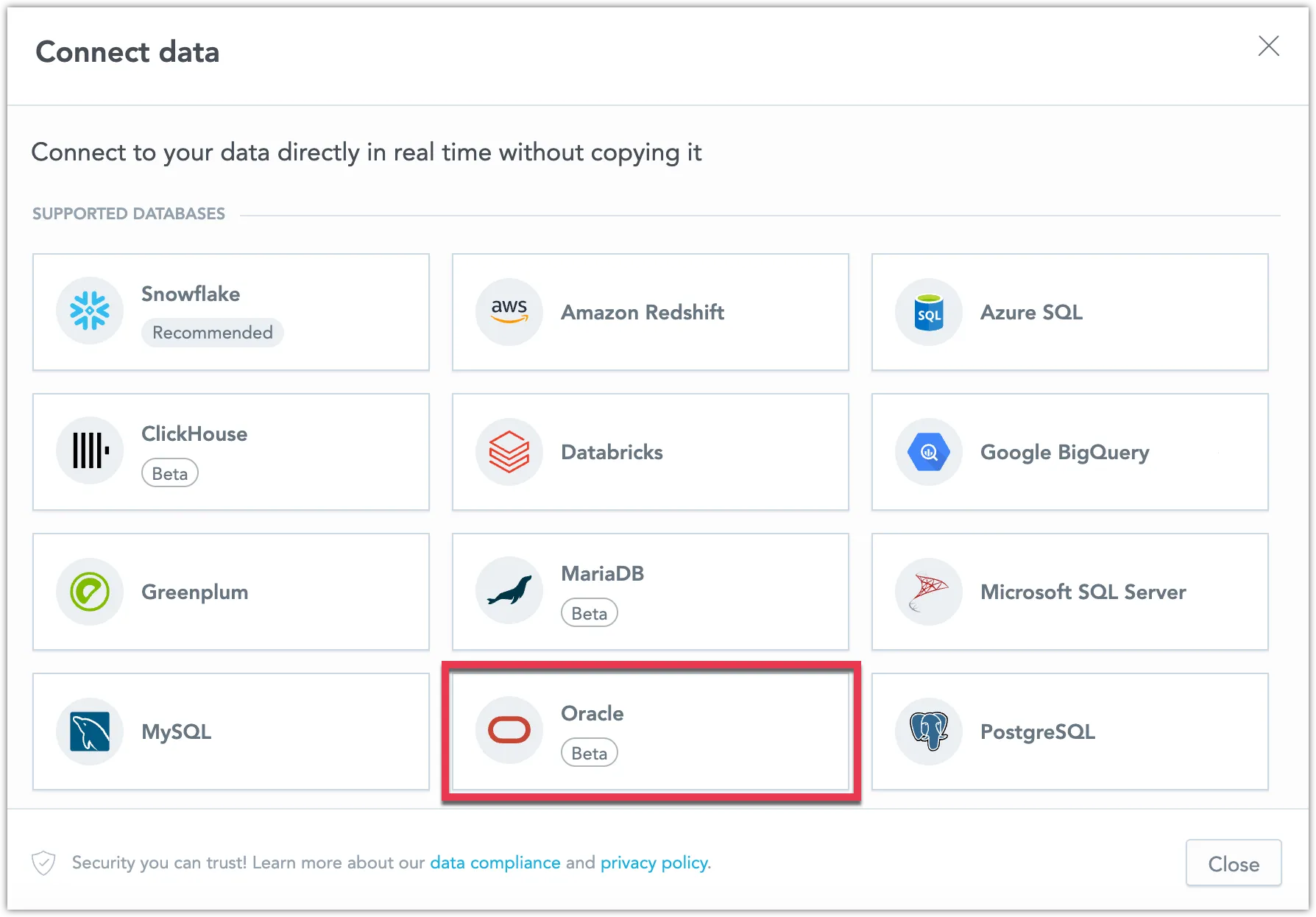
Select Oracle.
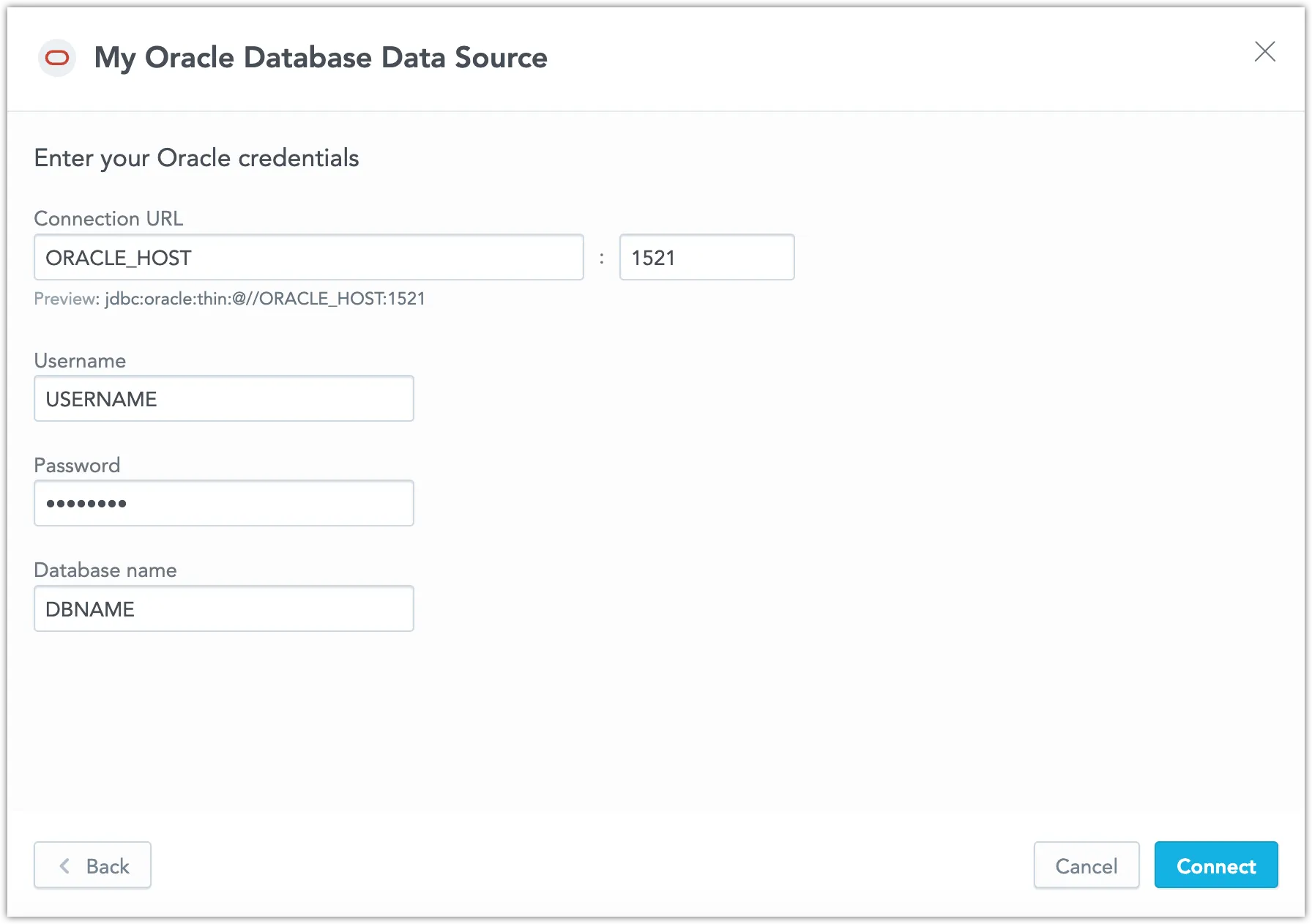
Name your data source and fill in your Oracle Database credentials and click Connect:
Click Save.
Your data source is created!
Steps:
Create a Oracle Database data source with the following API call:
curl $HOST_URL/api/v1/entities/dataSources \ -H "Content-Type: application/vnd.gooddata.api+json" \ -H "Accept: application/vnd.gooddata.api+json" \ -H "Authorization: Bearer $API_TOKEN" \ -X POST \ -d '{ "data": { "type": "dataSource", "id": "<unique_id_for_the_data_source>", "attributes": { "name": "<data_source_display_name>", "url": "jdbc:oracle:thin:@//<ORACLE_HOST>:1521/<ORACLE_DBNAME>", "schema": "<ORACLE_DBNAME>", "type": "ORACLE", "username": "<ORACLE_USER>", "password": "<ORACLE_PASSWORD>" }}}' | jq .To confirm that the data source has been created, ensure the server returns the following response:
{ "data": { "type": "dataSource", "id": "<unique_id_for_the_data_source>", "attributes": { "name": "<data_source_display_name>", "url": "jdbc:oracle:thin:@//<ORACLE_HOST>:1521/<ORACLE_DBNAME>", "schema": "<ORACLE_DBNAME>", "type": "ORACLE", "username": "<ORACLE_USER>" } }, "links": { "self": "$HOST_URL/api/v1/entities/dataSources/<unique_id_for_the_data_source>" } }
Additional Information
Ensure you understand the following limitations and recommended practice.
Data Source Details
Typical JDBC URL may look like this:
jdbc:oracle:thin:@//<host>:<port>/<databaseName>Basic authentication is supported. Specify
userandpassword.
Unsupported Features and Limitations
GoodData does not currently support the following features:
- Adding years to weeks may fail in some cases
- Date arithmetic only supports up to ±99 units (for example +99 days will work, +100 days will not work)
- SSL is not yet supported