21 Customer Service KPIs You Need to Track


Summary
Strong customer service depends on clear, measurable insights. Performance indicators help teams understand how well they are meeting customer needs, how efficiently they are resolving issues, and how satisfied customers are with the support they receive.
This article breaks down the most important metrics to track, including satisfaction scores like CSAT and NPS, as well as operational indicators like response time and resolution rates. You will learn how these KPIs can reveal service gaps, improve workflows, and build long-term customer loyalty.
How we Created This List of Customer Service KPIs
It is no secret that optimizing your customer service can have a large, positive impact on your organization. An improved customer experience translates to increased customer loyalty, reduced customer service costs, and increased revenue growth (through retention and upsell).
However, at a time when more and more data is collected, analyzed, and digested than ever it can be a challenge to choose which customer service metrics to measure in order to track performance and make improvements.
Of course, every customer service organization is unique. While some metrics will certainly be organization-specific, a selection of customer experience KPIs is helpful to track and measure as a baseline from which you can expand your list in line with your goals and needs.
At GoodData, we’ve seen hundreds of implementations of customer service analytics and as such, we wanted to share the most important KPIs for customer service we’ve observed. So, let’s take a look at 21 of the top metrics for customer service:
1. Number of New Tickets
One of the most obvious customer service KPIs to measure is the number of new tickets. It is incredibly important to measure the number of new tickets generated every day, week, month, and quarter. This enables managers to understand if new tickets are correlated to product launches and if they have enough employee bandwidth. Managers can also see how tickets compare historically.
2. Number of Resolved Tickets
With every new ticket comes (hopefully!) a resolved ticket. During a given timeline, if your organization receives more tickets than it can resolve, then your backlog will grow. Understanding this performance over time will enable managers to optimize and streamline their customer service team’s performance.
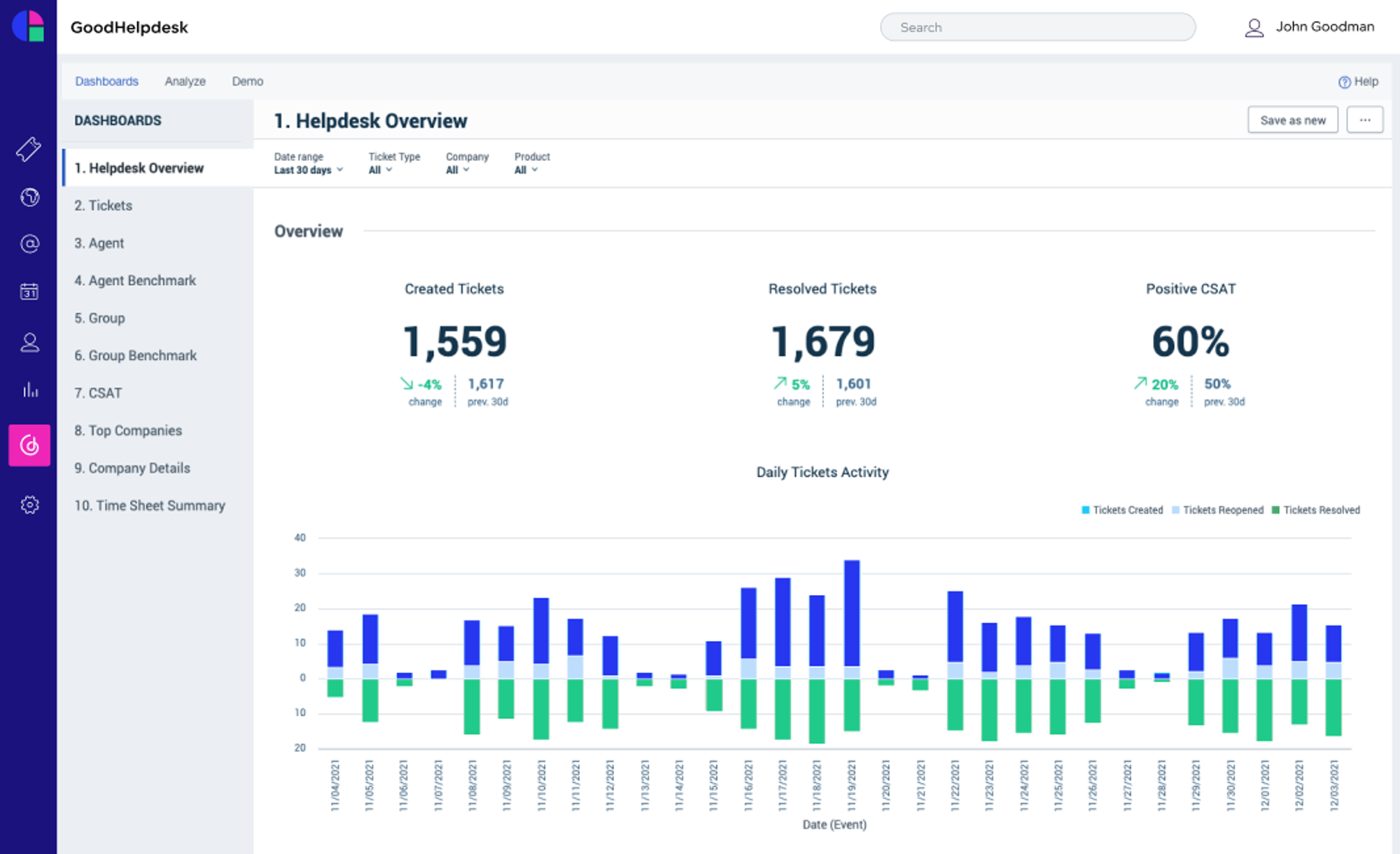
Customer helpdesk dashboard
3. Average Resolution Time
We understand that average resolution time is not a perfect metric. However, this is a support KPI that is extremely useful to track over time. As your business grows or has issues, managers need to understand the general trend of how long the ticket resolution rate is. This enables them to ask and answer questions like:
- How long will it take to reduce my backlog this quarter?
- Why has my average resolution time gone up 50% over the last quarter?
Understanding the average resolution time can help understand how to make customer service more efficient.
4. Consistent Resolutions
In addition to resolution times, another important customer service metric is ensuring consistent resolutions to customer queries. Picture your customer service operation as a production line, whereby the delivered product is of the same quality every time. In other words, regardless of which agent is in touch with a customer — be it via chat, email, or phone – the answers provided to the same issue are consistent across the board.
5. Cost Per Resolution
Calculating the cost of resolving each customer support ticket is crucial to understanding your operational and staffing costs. To calculate this customer service metric, you simply take the sum of your department costs for a given time period and divide it by the number of resolved tickets for the same time period.
Total operating expenses / # of tickets resolved = Cost per resolution
For example, if your total operating costs are $10,000 per month and your customer service team resolves 1,000 tickets, your cost per resolution would be $10.
Another similar customer service metric would be to look at the cost per ticket, whereby you would include all tickets open and resolved for a given time period and compare this with the above.
6. First Contact Resolution Rate
First contact resolution (FCR) or first-touch resolution, is the percentage of customer support tickets that agents resolve on first contact with the customer — and therefore, avoid the need to follow up later or transfer customers to other agents. This service desk KPI indicates efficiency, but remember that complex problems require more touches.
7. Top Topics
Recording and understanding the main reasons why customers contact your help desk is equally as important as the resolution time customer KPI. Tracking these topics will better inform you as to what customers are having issues with and what the root cause might be. For example, it might be that you have a gap in your instructions or documentation. Whatever the reason, you’ll be better equipped to find your flaws and make the necessary changes.
8. Escalation Rate
The escalation rate customer service KPI represents the number of tickets (as a percentage) that have been escalated to a person with more in-depth knowledge or experience — this could be a team lead, manager, or specialist in a certain area. It can be used to gauge the level of expertise your support team has and, for example, equips you to make more informed hiring decisions.
9. Customer Retention Rate
An organization’s ability to retain customers is key to its long-term success and is crucial for predictable revenue and profit. It also positively impacts other key customer service performance metrics like Net Promoter Score (NPS) and Customer Satisfaction Scores (CSAT).
To calculate your customer retention rate, use the following formula:
[(# Customers at End of Period – # Customers Acquired During Period) / # Customers at Start of Period] x 100
10. Net Promoter Score
Net promoter score (NPS) is a customer satisfaction metric that provides a benchmark of how likely your customers are to recommend your organization to somebody else. The NPS score is derived by asking your customers “How likely are you to recommend [company name] to a friend on a scale of 1 to 10?” The scores break down into the following categories:
- "Promoters" who provide ratings of 9 or 10
- "Passives" who provide ratings of 7 or 8
- "Detractors" who provide ratings of 6 or lower
Calculating the final net promoter score involves subtracting the percentage of detractors from the percentage of promoters collected by the survey item (the passives are scored neither positively nor negatively).

Net Promoter Score (NPS) By Bquast - Own work, CC BY 4.0, Link
A derivative of NPS is eNPS, which measures employee satisfaction. It is a quick and simple way to understand employee happiness.
11. Customer Effort Score
Customer Effort Score (CES) refers to the amount of effort a customer has to spend to resolve an issue. This could be how long it takes them to find the answer to their problem in your knowledge base or documentation, or how much time they need to spend communicating with you. To measure the CES customer KPI, companies typically ask customers to fill out a CES survey with questions including:
- On a scale of 1-10, how easy was it to resolve your issue with us today?
- Is there any way we could have helped you better?
- Were you able to accomplish your goal?
12. Customer Satisfaction Score
Outstanding customer service teams need to keep a constant pulse of their customer satisfaction (CSAT) score. This is the best measurement of how your service organization continues to perform. By providing an opportunity for customer feedback, managers can learn from said feedback to help them build and develop their customer service teams.
13. Top Agents
Finding out who your top-performing agents are is critical to building a healthy customer service organization. By measuring the number of tickets resolved, average handle times, and customer satisfaction –- managers can benchmark agents. This not only creates a healthy level of competition but also identifies any agents that may need additional care to meet their job requirements. This is just one of several call center agent performance metrics that can help drive your team's performance.
14. Knowledge Base/Documentation Engagement
Tracking the number of views and more importantly, the engagement rate of your knowledge base and/or documentation is an important KPI for customer service. The more engaged traffic your resources get, the higher the likelihood of customers finding the answers to their questions without needing to reach out directly to your customer service team. It also helps to understand how your documentation is performing and where you need to improve certain areas.
15. Abandonment Rate
Abandon rate, or call abandonment rate, is one of several call center metrics you should track. It represents the number of customers who hang up while on hold with customer support. This call center KPI can be calculated by finding the difference between calls received and handled calls and then simply dividing that by the total number of calls received.
[(Number of calls received – Number of calls handled) / Number of calls received] x 100
16. Agent Touches Per Ticket
Agent touches refer to any time a support team member interacts with a customer ticket. This is defined differently from company to company, but typically includes actions like replying to a customer, commenting on a ticket, or reopening/reassigning a ticket.
17. Number of Tickets by Medium
Historically, you may have seen most of your tickets issued through call centers as most consumers were conditioned to call a customer support number. However, more and more customers have now turned to contact forms, e-mail, and chat consoles. Knowing where your customer service team should invest more resources helps address customer issues quickly, leading to happier customers.
18. Top 10 Customers by Active Tickets
Do you know which customers you need to pay the most attention to? This is important not only to reduce your ticket backlog but also to help with customer satisfaction and retention. If you can identify your customers and how many tickets they have, you may be able to answer multiple questions at once. As a result, you can increase your customer service team's efficiency and strengthen your relationship with the customer.
19. Top Customers in Need
Equally as important as tracking your top 10 customers is knowing which 10 customers are most likely to churn. These customers may require a manager's attention. Or, they may have the most number of outstanding support requests, a significantly high handle time, or low customer satisfaction scores. Whatever the reasons may be, ensure you have a constant handle on this customer retention KPI, particularly if any of these customers form a large percentage of your revenue.
20. Response Time by First Reply
How long does it take for you to get back to customers? Minutes, hours, days? Customers expect a high level of engagement from their vendors. Even if you can't solve their problem during your first response, just letting the customer know that you have acknowledged the problem builds trust. Over time, as your organization becomes more and more efficient, this number should continue to trend down.
21. Average Handle Time
Even if you do respond quickly to an issue, how long is your average handle time? Acknowledging the issue is only half the battle. Customers should be kept in the loop of any resolution that your team is working towards. There should be many touchpoints and, if necessary or possible, a quick resolution. A low average handle time may also be a customer satisfaction KPI to track.
Explore more customer support and service desk KPIs
As well as those mentioned, there are likely other customer experience KPIs crucial for your customer service teams. At the end of the day, it's all about listening to your customers and doing whatever you can to assist them.
After all, it can cost up to five times more to acquire a new customer than to retain an existing one, so it stands to reason that even if you have some customers who require a little more attention, it is certainly worth investing in your customer service department to improve the overall experience.
Before tracking any customer service metrics, make sure that your executives and managers are aligned on what to measure and what results you expect.
Learn more about customer service analytics
Interested in how GoodData can help you better track and improve customer satisfaction through analytics? Don’t just take our word for it, read how Zendesk and LiveVox have done it with analytics for customer service, or request a demo and let our team of experts take you on a guided tour of the GoodData platform.
FAQs About Customer Service KPIs
CSAT (Customer Satisfaction Score) measures how satisfied customers are with a specific support interaction. It helps teams evaluate service quality and identify areas where customers feel well supported versus those needing improvement.
This metric tracks how long it takes to send the initial reply to a customer inquiry. Faster responses increase trust and prevent frustration, setting a positive tone from the start
FCR indicates the percentage of support issues resolved during the first interaction. High FCR means customers get answers immediately, which boosts satisfaction and reduces follow‑up tickets.
CES measures how easy customers find it to resolve their issues with your support. Lower effort typically correlates with higher satisfaction and loyalty, making interactions smoother and more efficient.
Escalation rate shows how often tickets are passed up to more senior agents; high rates may indicate training gaps. Churn rate helps assess whether unresolved or inefficient support experiences are causing customers to leave.


