Business Intelligence vs. Data Analytics: Which Do You Need?
Written by Tom Czaban |

Table of Contents
- What is Business Intelligence?
- What is Data Analytics?
- Business Analytics vs. Data Analytics: What's the Difference?
- AI in Business Intelligence vs. Data Analytics
- BI vs. Data Analytics: Which Is Right For You?
- BI Platforms vs. Modern Data Analytics Tools
- Why Choose GoodData as Your BI and Data Analytics Tool?
People tend to use the terms business intelligence (BI) and data analytics interchangeably, thinking they’re the same thing. However, there are some important differences. Once you understand them, you realize the real question isn’t just “What are business intelligence and analytics?” but more, “Which one does your business need — and when?”
This article breaks down business intelligence vs. data analytics with real-world examples to help you understand which you require (spoiler alert — in today’s business environment you’ll likely need both!)
BI vs. Data Analytics: A Beginner’s Cheat Sheet
- Business Intelligence answers: “What happened?” and “Where do we stand?”
- Data Analytics answers: “Why did this happen?” and “What should we do next?”
- BI Platforms usually focus on the front end, delivering interactive dashboards, reports, and visualizations to help businesses track performance.
- Data Analytics Platforms may offer an end-to-end approach, integrating structured and unstructured data from multiple sources, enabling deeper analysis, predictive insights, and AI-driven decision-making.
What is Business Intelligence?
Business intelligence (BI) is the process of collecting, analyzing, and visualizing structured data to track performance and support decision-making. It helps businesses transform raw data into actionable insights, allowing them to identify trends, measure success, and optimize operations. By leveraging BI, companies can make data-driven decisions rather than relying on intuition or guesswork.
Key features of BI include dashboards, KPI tracking, and historical data analysis. These tools make it easier for organizations to monitor performance in real time and spot patterns that inform future strategies.
BI is particularly useful for companies focused on operational efficiency. For example, an e-commerce company might use BI to track sales trends, analyze customer behavior, and optimize inventory levels, ensuring they always have the right products available at the right time.
Another example is in finance, where BI can help teams monitor performance and manage investments. For instance, Mercatus provides investors with the data and insights needed to better manage their assets, funds, and portfolios.
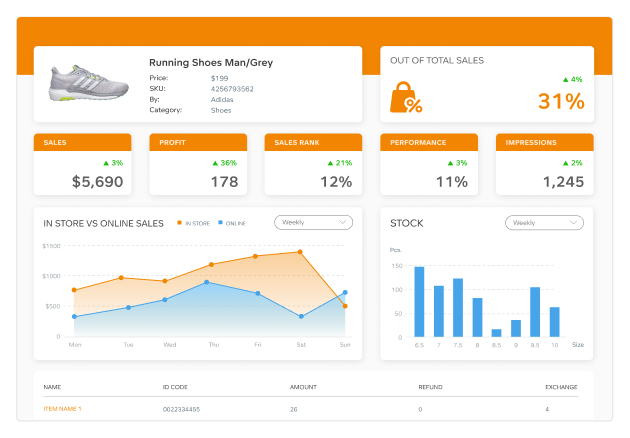
BI dashboard showing retail metrics
What is Data Analytics?
According to Gartner, “Analytics has emerged as a catch-all term for a variety of different business intelligence (BI) — and application-related initiatives … Increasingly, “analytics” is used to describe statistical and mathematical data analysis that clusters, segments, scores and predicts what scenarios are most likely to happen.”
Another way of looking at it is that data analytics builds on everything business intelligence (BI) offers — but with greater complexity and capability. It involves collecting, organizing, processing, and visualizing big data to uncover patterns, solve problems, and make predictions.
A key difference between BI and data analytics for business is the depth of insights provided, with analytics offering more advanced predictive and prescriptive capabilities. The back end is crucial here; effective data analytics require a well-governed system that efficiently manages large volumes of data. Data mining also plays a key role in this process, helping to identify hidden patterns and correlations within large datasets.
While data analytics is widely used in business, its impact extends across industries, including financial services, education, human resources, supply chain management, and scientific research.
There are three main types of data analytics:
- Descriptive analytics – Answers “What happened?” Similar to BI but with more flexibility in data exploration.
- Predictive analytics – Answers “What’s likely to happen next?” by identifying trends and forecasting future outcomes.
- Prescriptive analytics – Answers “What actions should we take?” by recommending the best course of action based on data.
Data analytics is particularly valuable for organizations that want to move beyond dashboards and drive innovation. Innovative software companies, for example, use predictive analytics to anticipate trends and optimize operations.
A good use case example is Fravebot, which helps commercial greenhouse growers forecast future yields to improve production efficiency. While in healthcare, providers use data analytics to detect anomalies and predict patient risk factors, improving early intervention and treatment planning.
Business Analytics vs. Data Analytics: What's the Difference?
Business analytics is an offshoot of data analytics that focuses on turning insights into strategic actions to improve business outcomes. While data analytics identifies patterns and trends, business analytics tends to go further by using techniques like scenario modeling to determine the best course of action. For example, a CMO might test different marketing strategies to maximize revenue, without having to see them all play out in real life.
Predictive analytics in an analytics platform
AI in Business Intelligence vs. Data Analytics
AI plays a significant role in both business intelligence and data analytics. In BI, AI primarily enhances automation, making it easier to analyze historical data and generate reports with minimal effort.
For example, an AI-driven BI tool might automatically update financial dashboards or generate sales performance reports, highlighting key metrics without manual input. This streamlines workflows and ensures businesses always have up-to-date insights.
The same can be said for data analytics, but it also uses AI and machine learning for deeper analysis and predictive insights. AI helps identify correlations and generate actionable forecasts, providing a forward-looking approach to data-driven decision-making. A retailer, for example, might use AI-powered data analytics to forecast demand and optimize inventory. By analyzing past sales patterns, seasonal trends, and customer behavior, AI can predict future product requirements, helping them to stay ahead of demand.
BI vs. Data Analytics: Which Is Right For You?
If your only objective is to monitor current operations, track KPIs, and gain insights into historical performance, basic business intelligence may be all you need. But if your organization is looking to explore new opportunities, forecast future trends, or build a data product, data analytics is your best bet.
Typically, today’s businesses require a combination of BI and data analytics to achieve full visibility into their operations and remain adaptable in the face of rapid market changes. By integrating BI and data analytics, teams cannot only monitor current performance but also leverage predictive insights to drive strategic growth and innovation.
BI Platforms vs. Modern Data Analytics Tools
Traditional BI platforms tend to focus only on the front end and achieve this by connecting a semantic layer to a data model. A good modern data analytics tool should provide a more end-to-end approach, blending data, and offering advanced features such as smart caching to reduce data warehouse costs.
Most of the best modern solutions are designed to handle large, complex datasets, offering real-time access to both historical performance data and predictive models. This breaks down departmental silos, fostering collaboration and enabling both business leaders and analysts to make informed decisions based on current metrics and future predictions. With all this in mind, it’s worth considering whether your next BI tool should even be a BI tool at all.
Why Choose GoodData as Your BI and Data Analytics Tool?
As a platform built on analytics and business intelligence, GoodData integrates seamless access to historical data and predictive models, supporting current operations and future business strategies. Its analytics lake centralizes both structured and unstructured data, providing real-time insights, scalability, and enhanced collaboration across teams — all while ensuring cost-efficiency and strong data governance. If you’re after a modular, end-to-end analytics platform that offers a range of AI features and integrates seamlessly with existing tools, request a demo today.
Written by Tom Czaban |

